Navigating Inflationary Risk: Strategies for Evaluation and Response
Understanding the Landscape: Inflationary Risk Evaluation
In the intricate realm of finance, evaluating inflationary risk is a critical task for investors, businesses, and policymakers alike. This article delves into the nuances of inflationary risk evaluation, exploring its impact on various sectors and outlining strategies to navigate this dynamic landscape.
Unpacking Inflationary Risk Factors
Inflationary risk is influenced by a myriad of factors, ranging from macroeconomic indicators to global market dynamics. To effectively evaluate inflationary risk, it’s essential to dissect these factors. Understanding the interplay of elements such as interest rates, consumer demand, and supply chain disruptions provides a comprehensive view of potential inflationary pressures.
Central Banks’ Role in Inflationary Risk Management
Central banks play a pivotal role in managing inflationary risk through monetary policy. Their decisions on interest rates, money supply, and open market operations directly impact inflation. Evaluating central banks’ strategies and their response to economic conditions is crucial for forecasting and preparing for potential inflationary risks.
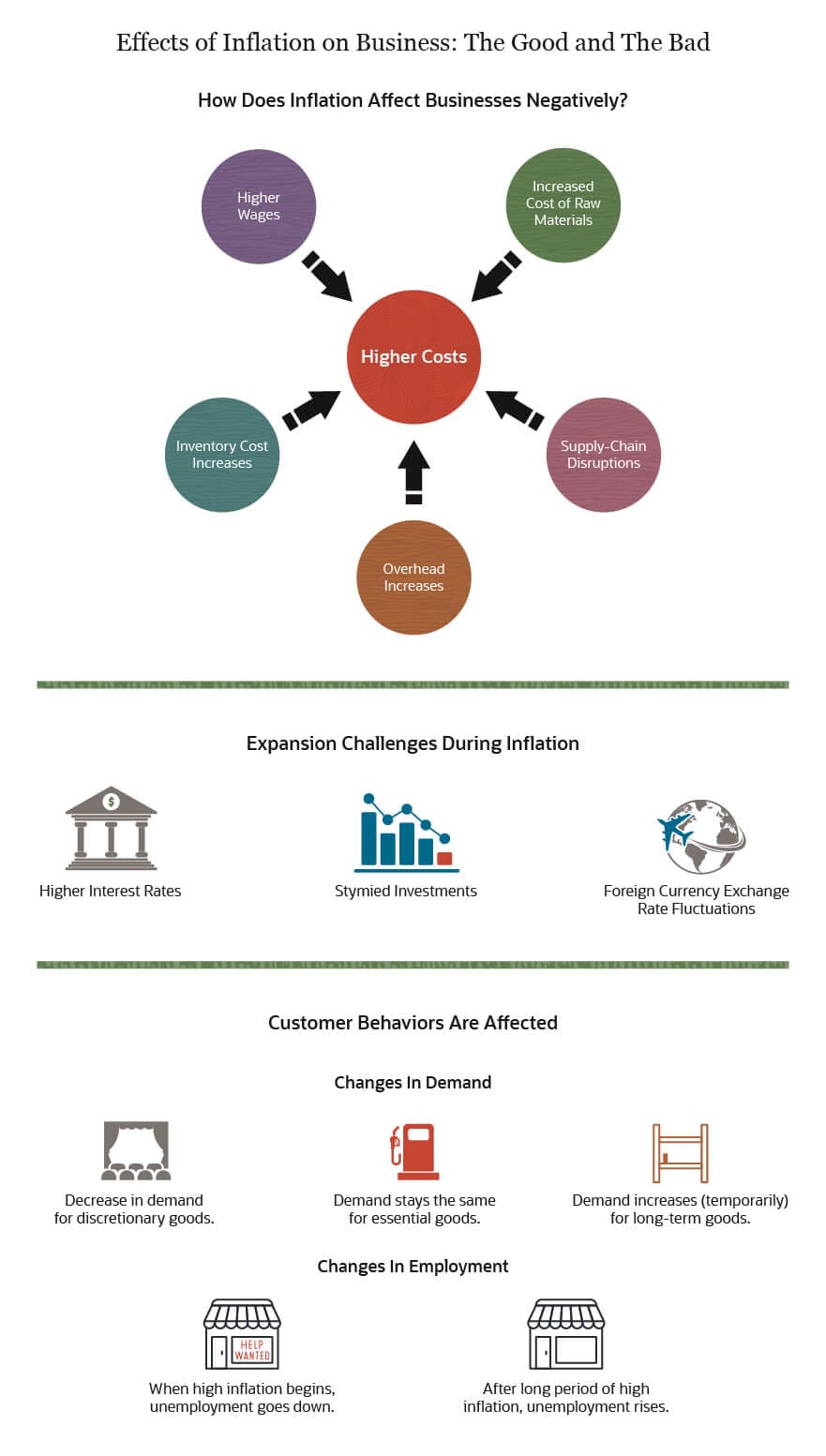
Impact of Inflationary Risk on Businesses
Inflationary risk can have profound implications for businesses. Rising costs of production, fluctuating commodity prices, and changes in consumer behavior are all factors businesses must navigate. Assessing the specific impact of inflationary risk on different industries enables businesses to develop resilient strategies to adapt to changing economic conditions.
Investor Considerations in Inflationary Risk Environments
For investors, inflationary risk introduces uncertainties into financial markets. Asset values, interest rates, and the overall risk-return profile of investment portfolios can be affected. Evaluating how different asset classes respond to inflationary pressures is essential for constructing well-balanced and resilient investment portfolios.
Real Assets as Inflationary Risk Hedges
Real assets, such as real estate and commodities, are often considered hedges against inflationary risk. Their intrinsic value and ability to retain worth in the face of rising prices make them attractive investments. Evaluating the role of real assets in a diversified portfolio is crucial for investors seeking to mitigate inflationary risk.
Global Economic Perspectives on Inflationary Risk
In today’s interconnected world, global economic perspectives shape inflationary risk. Factors like international trade dynamics, geopolitical events, and currency fluctuations contribute to the complexity of inflationary risk evaluation. Understanding the global context is paramount for anticipating and responding to potential inflationary pressures.
Government Policies and Inflationary Risk Mitigation
Government policies play a vital role in mitigating inflationary risk. Fiscal policies, including tax strategies and government spending, can influence inflation. Evaluating the effectiveness of these policies provides insights into the government’s approach to maintaining economic stability in the face of inflationary risk.
Technological Innovations in Inflationary Risk Assessment
In the digital age, technological innovations offer new tools for assessing and managing inflationary risk. Advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and big data enable more sophisticated risk assessment models. Evaluating the integration of technology into risk assessment processes enhances the precision of evaluating and responding to inflationary risk.
Accessing Real-time Insights for Informed Decision-Making
Staying informed in real-time is imperative for effective inflationary risk evaluation. Platforms like rf-summit.com offer valuable insights, analyses, and expert opinions on inflationary trends and risk