Understanding Inflationary Forces: An Overview of Economic Dynamics
Navigating Economic Currents: An In-Depth Exploration of Inflationary Forces
In the intricate tapestry of economic landscapes, understanding the forces that drive inflation is essential for informed decision-making by individuals, businesses, and policymakers. This article provides an insightful overview of the various inflationary forces shaping economic dynamics.
The Fundamentals of Inflation
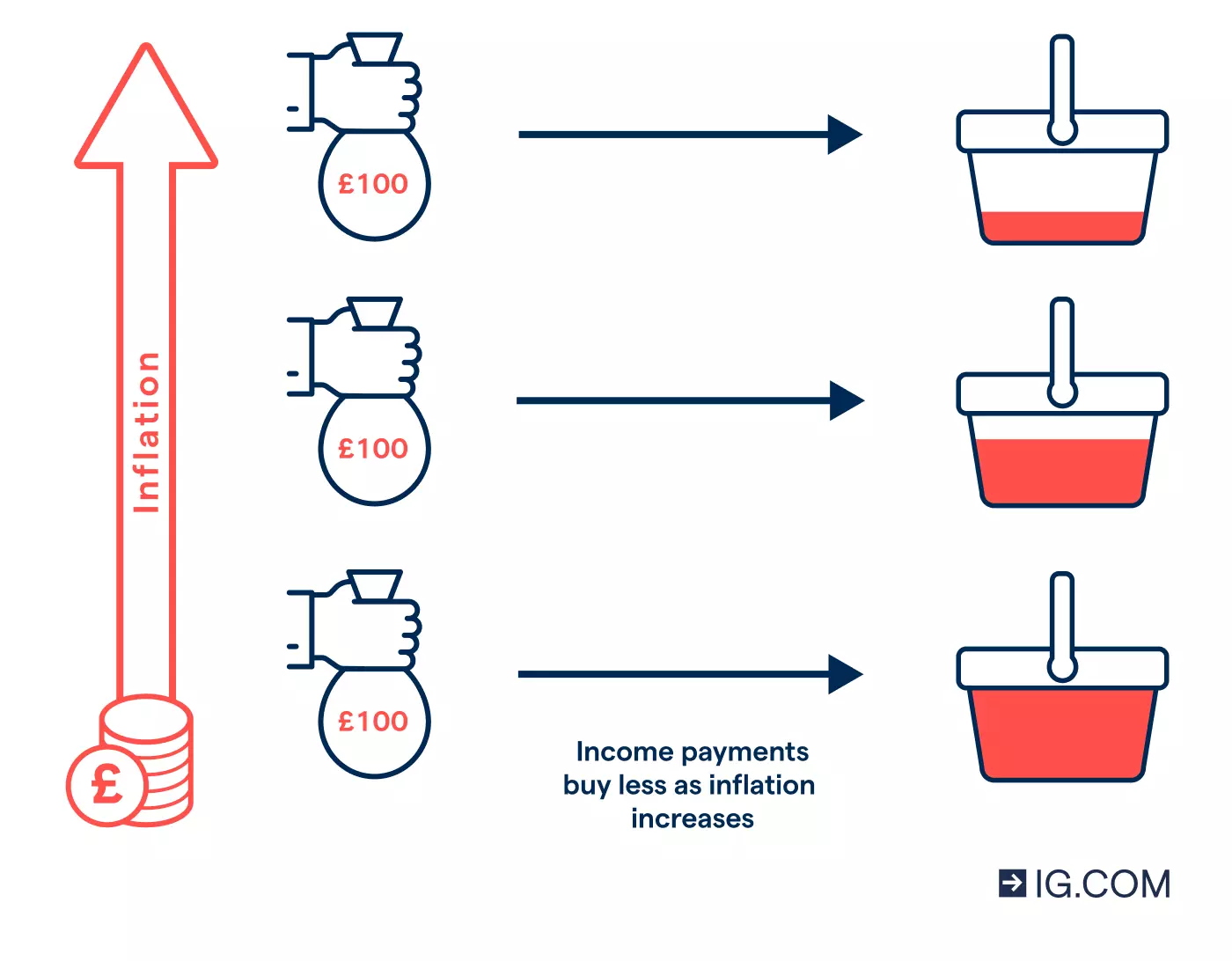
Inflation, the rise in the general price level of goods and services, is influenced by a combination of factors known as inflationary forces. Understanding these fundamentals is crucial for dissecting the intricate mechanisms that contribute to changes in prices and, subsequently, economic conditions.
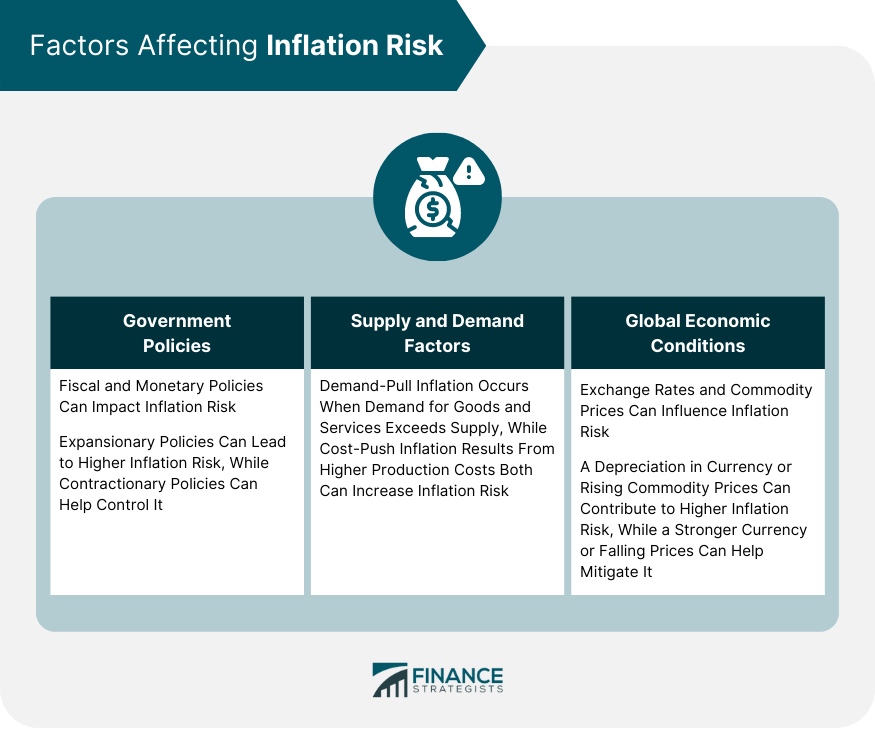
Demand-Pull Inflation: Consumer Power in Action
One significant inflationary force is demand-pull inflation. This occurs when consumer demand outpaces the available supply of goods and services. As demand rises, businesses may respond by increasing prices, contributing to an overall inflationary trend. Consumer spending habits and economic growth play pivotal roles in the dynamics of demand-pull inflation.
Cost-Push Inflation: Supply Side Pressures
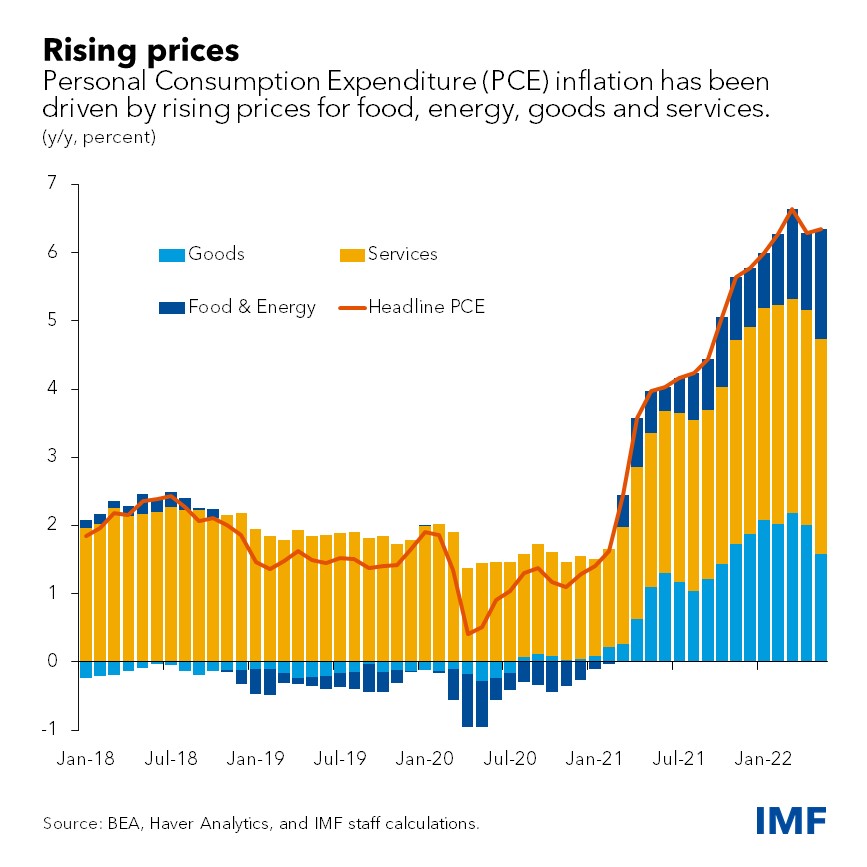
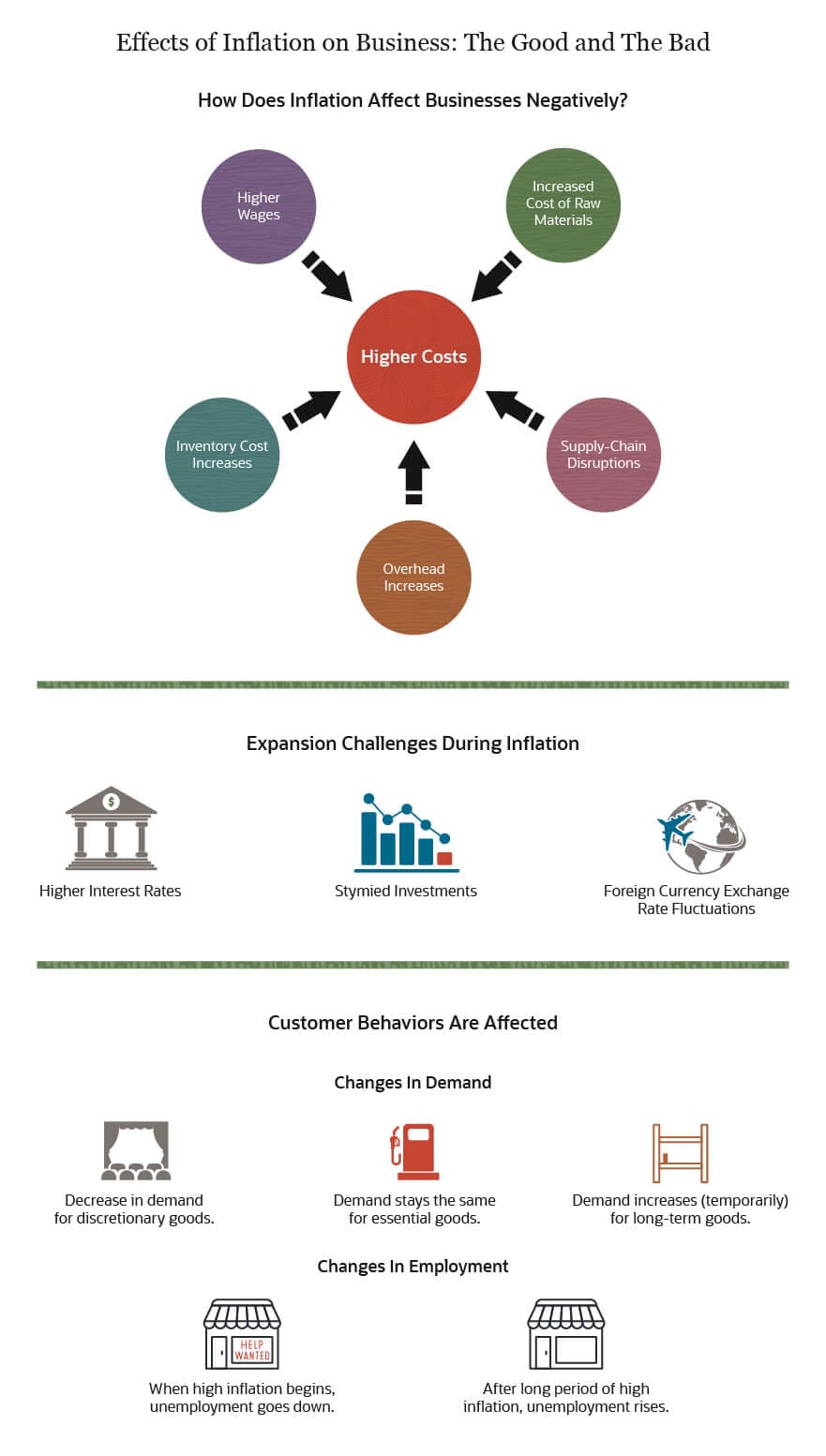
On the flip side, cost-push inflation stems from increases in production costs. Factors such as rising raw material prices, labor costs, or supply chain disruptions can lead businesses to raise prices to maintain their profit margins. Cost-push inflation highlights the impact of supply-side forces on overall price levels.
Built-In Inflation: Wage-Price Spirals
Built-in inflation, also known as wage-price inflation, involves a self-perpetuating cycle where rising wages lead to higher production costs, which, in turn, result in increased prices. The continuous loop of wage and price increases characterizes this inflationary force. Understanding the dynamics of wage-price spirals is crucial for addressing built-in inflation.
Monetary Policy and Inflation
The actions of central banks through monetary policy significantly influence inflationary forces. Adjusting interest rates, controlling money supply, and implementing other monetary measures impact the overall availability of money in the economy. The delicate balance between stimulating economic growth and preventing excessive inflation is a key consideration for policymakers.
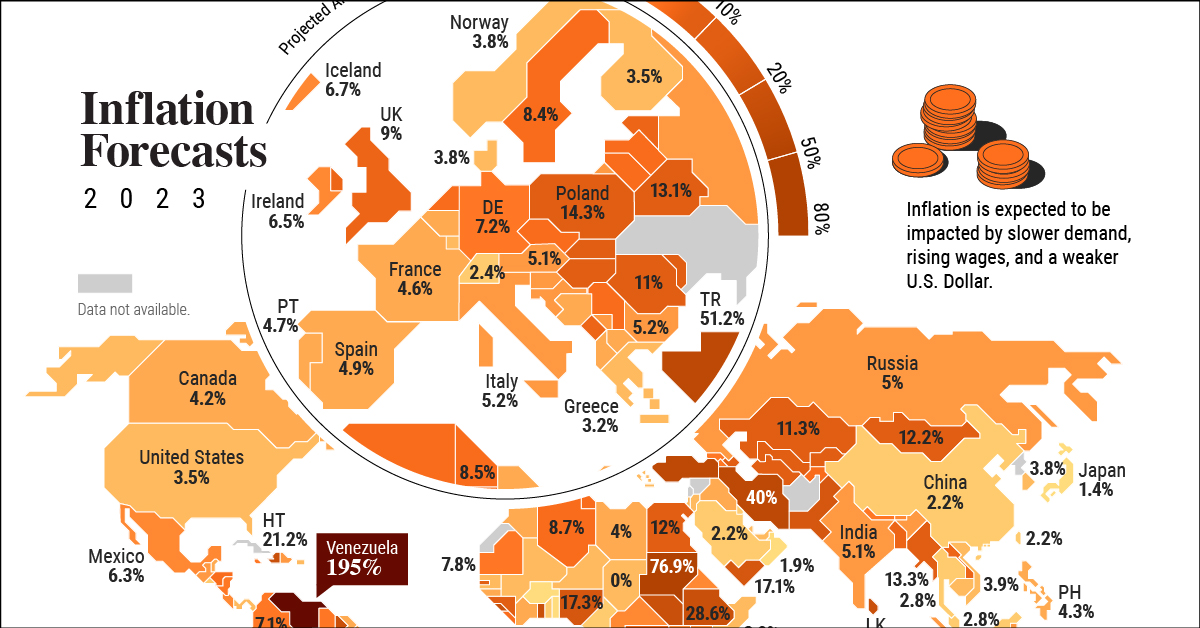
Global Economic Factors: The Impact Beyond Borders
In our interconnected world, global economic forces play a substantial role in shaping inflationary trends. Fluctuations in exchange rates, international trade dynamics, and geopolitical events can all contribute to inflationary pressures. Understanding the cross-border impact of these forces is vital for comprehensive economic analysis.
Technology and Innovation: A Double-Edged Sword
Technological advancements and innovation can act as both inflationary and deflationary forces. On one hand, innovations may increase efficiency and reduce production costs, mitigating inflationary pressures. On the other hand, disruptive technologies or supply chain innovations can contribute to inflation by altering demand-supply dynamics.
In-Depth Exploration of Inflationary Forces
For a comprehensive exploration of current trends in inflationary forces and expert insights, explore Inflationary Forces Overview. This resource provides valuable information to help individuals, businesses, and policymakers stay informed and make decisions aligned with the current economic climate.
Mitigating Inflationary Pressures: Strategies for Stability
In conclusion, navigating the complexities of inflation requires a nuanced understanding of the various forces at play. Whether driven by consumer demand, supply-side pressures, or global economic dynamics, each force contributes to the overall inflationary environment. By comprehensively analyzing