Market Dynamics: Navigating the Impact of Inflation
Navigating Economic Landscapes: Understanding the Impact of Inflation on Markets
In the intricate world of finance, the impact of inflation on markets is a crucial consideration for investors, businesses, and policymakers alike. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of how inflation influences market dynamics, affecting various assets and shaping investment strategies.
The Relationship Between Inflation and Market Behavior
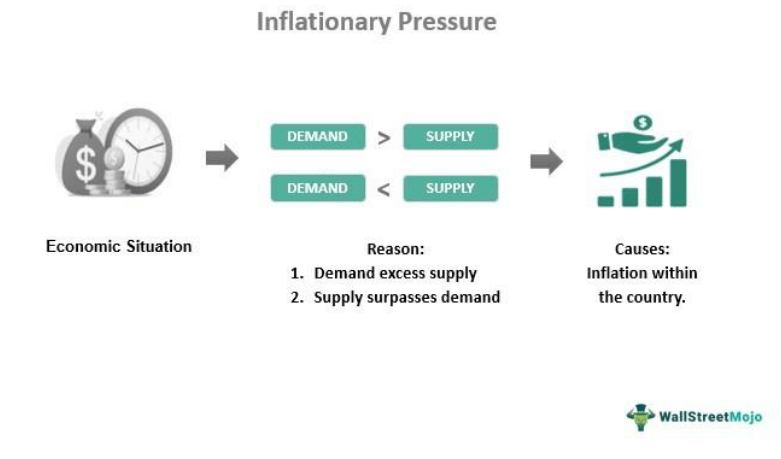
Understanding the impact of inflation on markets begins with recognizing the intricate relationship between these two variables. Inflation, the rise in the general price level of goods and services, can have profound effects on financial markets. Investors must navigate these effects to make informed decisions and optimize their portfolios.
Stock Markets: Inflation’s Double-Edged Sword
Stock markets experience a complex interplay with inflation. On one hand, moderate inflation can signal a growing economy, potentially boosting corporate profits and driving stock prices higher. However, excessive inflation may erode the real value of company earnings and decrease investor confidence, leading to market volatility.
Bonds and Fixed-Income Investments
The impact of inflation on fixed-income investments, such as bonds, is direct and pronounced. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of future interest and principal payments, resulting in reduced real returns for bondholders. Investors in fixed-income assets must carefully consider inflationary trends to protect their portfolios from value erosion.
Real Assets as Inflation Hedges
Real assets, including commodities and real estate, are often considered hedges against inflation. In times of rising prices, these tangible assets may retain or increase in value. Investors seeking to mitigate the impact of inflation on their portfolios often allocate a portion of their investments to real assets for added resilience.
Currency Markets: Inflation’s Influence on Exchange Rates
Inflation plays a significant role in shaping exchange rates in currency markets. Countries with lower inflation rates often see appreciation in their currency values, while those experiencing higher inflation may witness depreciation. Forex traders closely monitor inflation indicators to anticipate currency movements and make informed trades.
Central Bank Policies and Market Expectations
The impact of inflation on markets is intertwined with the policies of central banks. Monetary authorities, through interest rate adjustments and other measures, aim to manage inflation and stabilize markets. Investors closely analyze central bank actions and statements, as these can influence market expectations and asset valuations.
Investor Strategies in Inflationary Environments
Navigating the impact of inflation on markets requires strategic thinking from investors. Inflationary environments demand a reassessment of investment portfolios, with a focus on assets that historically perform well during inflationary periods. Diversification and active risk management become integral components of investor strategies.
Economic Indicators and Inflation Forecasts
Investors and market participants rely on economic indicators and inflation forecasts to gauge the potential impact on markets. Understanding leading indicators, such as consumer price indices and producer price indices, provides valuable insights into the direction and intensity of inflationary pressures, influencing market sentiment.
In-Depth Exploration of Inflation Impact on Markets
For a deeper exploration of the impact of inflation on markets and expert insights, explore Inflation Impact on Markets. This resource offers valuable